Digital TV business glossary & terms
The glossary below clarifies some abbreviations and terms you might come across while getting familiar with digital TV technology or business (e.g. DVB, OTT, VOD, HbbTV, Smart TV; see below). Hopefully, you'll find this glossary beneficial!
ACDEFGHIJKLMNOPRSTUVW#AIT
Application Information Table; a DVB table that includes the application URL and other related data. Used to signal HbbTV application in broadcast. Read how to signal HbbTV application with AITAndroid TV
Operating system (e.g. Smart TV) developed by Google, used in i.e. Sony, Philips, Sharp and Hisense TV's. Read more: Designing multiplatform Smart TV applications and Smart TV operating systemsAPI
Application Programming Interface; set of rules that enables third parties to obtain and change information or data of the service. When making a digital TV or any service, some APIs (e.g. to CRM) usually need to exist to be able to communicate between different systems.ASO
Analog switch-off; switching from analog transmission to digital. Read about Malaysian ASOATSC
Advanced Television Systems Committee; an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. Used also e.g. in South Korea. Latest standard version is ATSC 3.0, marketing name "NextGenTV", with support for more services, 4K UHD image and portable devices.AVOD
Ad-based Video On-Demand; offers consumers access to a catalogue of on-demand content and contains advertisements.A/B Testing
A/B testing is a user experience research methodology. In A/B testing, two or more different versions of the application are offered either randomly or to a controlled group, and manual feedback and automatic behavior analysis is collected and acted upon. A special form of A/B testing is also common practise when rolling out new features, to collect reactions to an improved or changed feature in the application.CAM
Conditional Access Module; device that enables watching scrambled (purchased) services, CAM has a slot for a smart card. The module is inserted into the PC Card slot of a TV or an STB.It now also exists in a USB format which is a modern form factor and addressing the global market. CAM can also trigger an HbbTV application in a simple way for the end user.
CAS
Conditional Access System; system to prevent unauthorized viewing of e.g. video material by content protection achieved by encrypting (scrambling).CAPEX (Capital Expenditure)
CAPEX monetization model involves funds used to acquire or upgrade long-term physical assets like property or equipment. These investments are not fully expensed in the purchase year but are depreciated over the asset's life, impacting long-term financial strategy.Catch-up
Feature that enables end-user to watch e.g. previous episodes of a series (via IP).CDN
Content Delivery (/Distribution) Network; optimizes content (e.g. video) accessibility globally by geologically distributed servers, usually including load balancing, analytics and artificial intelligence.CI+
Common Interface Plus; specification that extends the original DVB Common Interface standard (DVB-CI). The Common Interface is the connection between the TV/STB tuner and the module that decrypts the TV signal (CAM).CMAF
Common Media Application Format; standard intended to simplify delivery of HTTP-based streaming media and to especially avoid storing and encoding video data in several different formats.CMP
Consent Management Platform; a system or process for allowing customers to determine what personal data they are willing to share with a broadcaster or operator (related to GDPR). E.g., end-user must comply with certain minimal policies to gain the right to use an application.CMS
Content Management System; assists with storage and organization and makes it possible to share e.g. video assets on different platforms.CRM
Customer Relationship Management; required for subscription-based services (i.e. VOD) for identifying the customer.CSAI
Client-Side Ad Insertion; inserting (or stitching) the ad media at client side by making a call to an ad server at ad breaks. Enables highly personalized ads but is heavy for the server and susceptible to ad blockers.CSR
Central Service List Registry; a service list collection, combining all the available service lists in a single repository. Service lists are required by all devices implementing the DVB-I, like smartphones, tablets, PC's, TV's or STB's to access any service. These service lists may be operated by, or on behalf of, various kinds of organizations, such as the manufacturer of the device, a national or regional regulator, or an operator or platform brand serving only their own clients.CSS
Cascading Style Sheets; describes the presentation of an HTML document.CTV
Connected TV; any television set used to stream video over the internet.DAI
Dynamic Ad Insertion; video ad technology that allows you to serve video ads into live linear programming and video on demand content. Can be client-side (see CSAI) or server-side (see SSAI).DASH
Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP; an adaptive bitrate streaming technique that enables high quality streaming of media content over the internet using HTTP. Read about DASH reference applicationDASH-IF
The DASH Industry Forum (DASH-IF) is a system which according to the company "creates interoperability guidelines for the usage of the MPEG-DASH streaming standard. It consists of streaming and media companies, such as Microsoft, Netflix, Google, Ericsson, Samsung and Adobe." They provide an open source version of this software also.DRM
Digital Rights Management; controls the use and distribution of copyrighted works, commonly used systems in the area of video are e.g. PlayReady, Marlin and Widevine.DSM-CC
Digital Storage Media Command and Control; toolkit for developing control channels associated with MPEG streams, enables e.g. interactive commercials.DTH
Direct-to-home; can either refer to the communications satellites themselves that deliver service or the actual television service.DTT/DTTV
Digital Terrestrial Television; specific abbreviation for digitalized terrestrial TV.DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting; international open standard for digital transmissions. The DVB Project (dvb.org) is the maintaining organisation. Remark: There are well over a billion DVB receivers deployed all over the world! And the number is increasing all the time… Read about modern hybrid DVB PSI/SI & EPG generator (white paper)DVB-C/C2
Digital Video Broadcasting, Cable; international open standard for digital transmissions. DVB-C is common in urban areas, but the newer DVB-C2 is not currently used.DVB-HB
Digital Video Broadcasting, Home Broadcast; to enable consumption of traditional broadcast services (i.e., delivered via satellite, terrestrial or cable broadcast networks) by means of in-home networked devices, e.g., smartphones, tablets, Personal Computers, IP-enabled TV sets or Set-Top-Boxes etc.DVB-I
Digital Video Broadcasting, Internet; international open standard for digital transmissions. Delivers services over the Internet to devices with broadband access, device can also have a DVB tuner. Read about DVB-I solutionDVB-S/S2
Digital Video Broadcasting, Satellite; international open standard for digital transmissions. DVB-S broadcasting started the mid-1990s and is still going strong.DVB-T/T2
Digital Video Broadcasting, Terrestrial; international open standard for digital transmissions. DVB-T2 is more advanced and efficient and will gradually replace DVB-T.EIT
Event Information Table; a DVB table holding program information, the start and end time with the program description, possible age restriction etc. The EPG consists of EIT data.EPG
Electronic Program Guide; an application to show EIT information (e.g. title, description, rating) of broadcasted programs or other video assets, OR sometimes also meaning the actual TV program or video asset metadata. Read about EPG Management productFAST
Free ad supported TV; A free-to-use TV channel supported only by advertisements or other kind of subsidy and/or sponsorship. Gaining in popularity and variety, usually distributed over the IP as part of other service offering. Really just a new acronym for the oldest form of linear TV service.FTA
Free-to-air; free/clear (no cost) channels available to everyone (versus encrypted/subscribed).GDPR
General Data Protection Regulation; The European Union (EU) has enhanced individuals' control and rights over their personal data (since May 2018), this affects services where users must be identified. If e.g. a website holds user data of EU citizens (name, cookies etc.), the end-user must provide a valid consent for this purpose.Google TV
The Google TV platform is the successor of Android TV. This could also be called rebranding or renaming due to the fact that the underlying software remains the same. There are nonetheless many changes, and now the focus will be on personalized content and tailored recommendations. The most noticeable change is the new user interface, which puts content first. It is predicted that from 2022 onwards all Google-based devices will be using Google TV instead of Android TV. Read more: Smart TV operating systemsHbbTV
Hybrid Broadcast Broadband TV; standard for interactive services on top of DVB, widely used especially in Europe. HbbTV enables ample offering of services on TV. Read about how to enable HbbTVHD(TV)
High Definition (Television); screen resolutions from 1280x720 up to 1920x1080. See also other resolutionsHLS
HTTP Live Streaming; HTTP-based adaptive bitrate streaming communications protocol developed by Apple Inc. Adaptive streaming adapts to the available network bitrate and adjusts the image resolution.HTML5
Hyper Text Markup Language version 5; the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. Version 5 is more mobile-friendly, supports audio and video controls, vector graphics, canvas support, localStorage, track geolocation etc.HVOD
Hybrid VOD: a combination of AVOD and SVOD, where it is possible to have a lower SVOD subscription price if some advertisements are shown. Can also be a combination of AVOD and SVOD content under a single subscription.Hybrid TV
Combining interactive TV implemented using broadband (via IP) with broadcast (via tuner). HbbTV apps are considered Hybrid TV services.IP
Internet Protocol; the principal protocol by which data is sent from one computer to another on the Internet.ITV
Interactive TV; data services added to television using IP and thus making it interactive.javaScript
Programming language widely used in digital TV services, both in HbbTV and Smart TV. Used alongside HTML and CSS.MHEG
Multimedia and Hypermedia Experts Group; nowadays usually found in the form "MHEG-5", which refers to interactive applications on TV based on the MHEG-5 standard, used especially in the United Kingdom.MHP
Multimedia Home Platform; the first open middleware system standard (end of 1990s/early 2000s) designed by the DVB project for interactive digital television. HbbTV has substituted MHP in many areas, though MHP applications still exist in some countries.MPEG
Moving Picture Experts Group; literally refers to the group of authorities, but more commonly to compression formats used in digital TV: MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 AVC, HEVC etc.NetCast
Proprietary firmware by LG Electronics that was preinstalled on their smart TVs between 2007 and 2014. Later replaced by WebOS.NorDig (group)
Represents broadcasters and network operators in the Nordic countries and Ireland that have, e.g., agreed on common minimum decoder requirements. A few other countries have also based their STB requirements on this specification.NPVR
Network Personal Video Recorder; network-based digital video recorder stored at the provider's central location rather than at the consumer's private home (PVR).Object-oriented programming (OOP)
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a paradigm where programs are composed of "objects"—data structures encapsulating data fields and methods. Key concepts include classes (blueprints for objects), inheritance (objects inheriting features from other classes), and polymorphism (objects treated as their abstract class type).OpApp
Operator Application; a special HbbTV application that defines operator-specific appearance and functions without a separate STB, acts like "virtual STB" built on smart TV. Read about OpApp caseOPEX (Operational Expenditure)
OPEX monetization model refers to the ongoing, daily expenses required to run a business, like rent, utilities, and salaries. These costs are short-term, recurring, and fully tax-deductible in the year they occur, emphasizing operational efficiency.OTA
Over-the-air; delivery of new software, firmware, to TV or STB via broadcast.OTT
Over-the-top; a platform or application to provide a set of TV and video services (VOD, start-over etc.) over IP, also to “companion screens” (tablets, mobile phones). Read about OTT platformPSI/SI
Program Specific Information/Service Information; crucial data and metadata for digital transmissions. Specification for Service Information (SI) in DVB systems. Read about how to manage PSI/SIPVR
Personal Video Recorder; a type of STB that allows recording of TV programs. Presence of scheduled EPG data is essential with this.SCTE-35 and -104
Society of Cable and Telecommunications Engineers; non-profit professional association for the advancement of technology, standards and workforce education related to cable telecommunications engineering. "SCTE-35 markers" indicate where downstream systems can insert other content (usually advertisements or local programs). SCTE-104 is used in the head-end side, SCTE-35 in the transmitted signal. See also TA/DVB-TASD(TV)
Standard Definition (Television); screen resolutions from 704×480 up to 720×576. See also other resolutionsSmart TV
A modern digital TV with several built-in applications including a browser and normally also HbbTV support. Read about TV applicationsSSAI
Server-Side Ad Insertion; a way of stitching an ad directly into the video that is being streamed – at the server instead of the client. This eases the load on the server and makes ad blocking difficult, but the ads it enables are less personalized.SSU
System software update; a method to update STB/Smart TV system software via broadcast.Start-over
Feature that provides a way to start an ongoing broadcast program from the beginning (via IP).STB
Set-top box; integrated digital receiver, a device able to receive a digital TV signal and transform it into a clear TV picture.SVOD
Subscription Video on Demand; consume as much video content as you want with a monthly payment.TA/DVB-TA
Targeted Advertising; a method to better monetize service offering by serving personalized and targeted ads to consumers. DVB-TA is the DVB Project’s specification for broadcasters who wish to dynamically substitute advertising in a linear broadcast over traditional DVB networks or IP networks.Tizen
Operating system (e.g. Smart TV's, smartwatches) used by Samsung since 2012. Most popular Smart TV platform globally (13%; 2020). Read more: designing multiplatform Smart TV applications and Smart TV operating systemsTS
(MPEG) Transport Stream, also known as multiplex or mux; comprised of video, audio and data/metadata, contains several TV/radio programs. The packet format used for DVB and HLS transport.TVOD
Transactional Video on Demand; consumers purchase content on a pay-per-view basis, especially latest movies etc.UHD
Ultra-high Definition TV (also known as 4K UHD); screen resolution 3840x2160. See also other resolutionsVAST
VAST is a Video Ad Serving Template for structuring ad tags that serve ads to video players. Using an XML schema, VAST transfers important metadata about an ad from the ad server to a video player. Initially launched in 2008, VAST has since played an important role in the growth of the digital video marketplace.VMAP
The IAB Video Multiple Ad Playlist (VMAP) specification is an XML template that video content owners can use to describe the structure for ad inventory insertion when they don’t control the video player or the content distribution outlet.VOD
Video on Demand; service for providing a wide variety of video material (series, movies) to end-users, letting them decide when to watch. Subscription often required, but public broadcasters may offer service for free.WebOS
Operating system (e.g. Smart TV) initially developed by Palm Inc. (which was acquired by Hewlett-Packard) for mobile devices, later sold to and patents licensed to LG Electronics. Read more: designing multiplatform Smart TV applications and Smart TV operating systems576p, 720p, 1080p, 2160p, 4320p
576p = 720x576 video screen, representing SD image. 720p = 1280x720 video screen, representing HD image. 1080p = 1920x1080 video screen, representing HD image. 2160p = 3940x2160 video screen, representing 4K UHD image. 4320p = 7680x4320 video screen, representing 8K UHD image.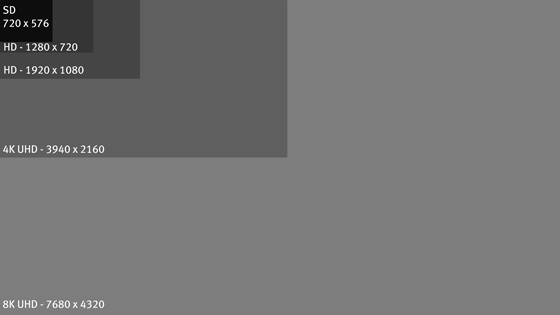

Juho Mäyränpää
Sales director
+358 50 522 5420
juho.mayranpaa@sofiadigital.com